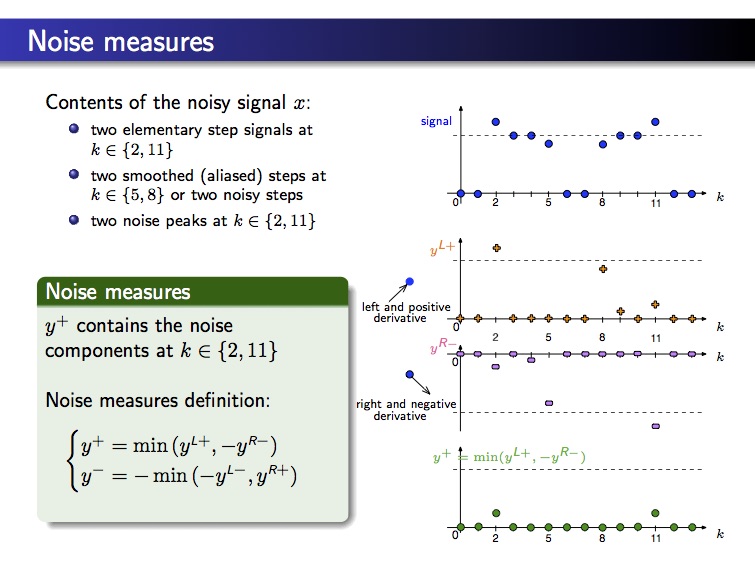
A noisy image and noise measure images
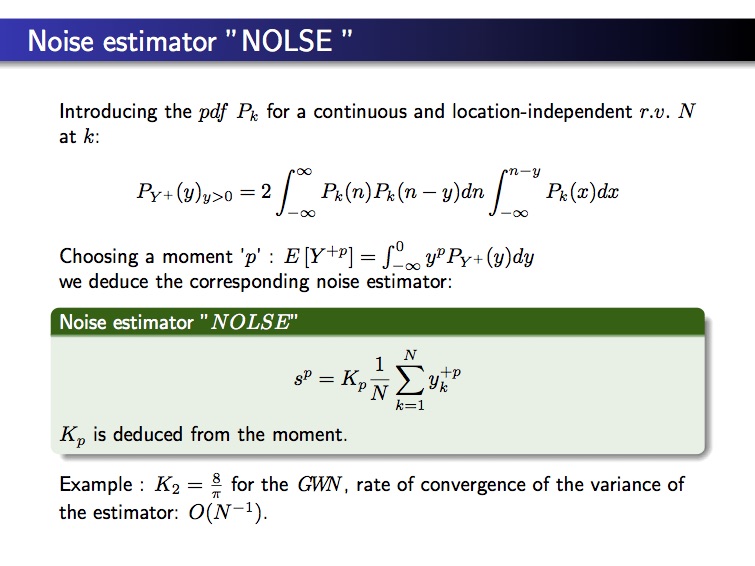
The NOISE ESTIMATOR NOLSE
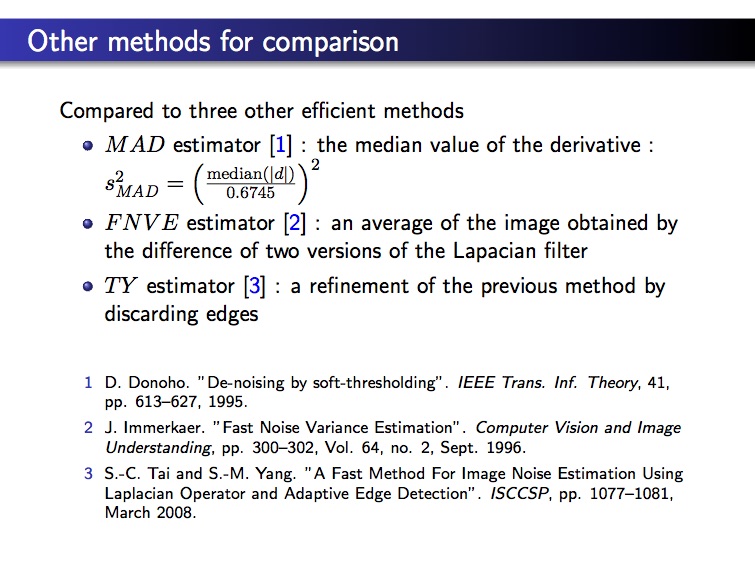
A METHOD INHERTIED FROM THE NON LINEAR DERIVATIVE
- a noise estimator based on the step signal model
- uses polarized/directional derivatives and a nonlinear combination of these derivatives to estimate the noise distribution (Gaussian, Poisson, speckle, etc.)
- does not rely only on the smallest amplitudes in the signal or image
- efficient for any distribution of noise : does not make assumptions regarding the distribution of the noise and is able to measure additive noise as well as multiplicative noise, salt-and-pepper noise, etc.
- the moments of this measured distribution can be computed and are also calculated theoretically on the basis of noise distribution models
- the asymetry of the noise distribution can be accurately estimated if the noise distribution is not dense as in the case of salt-and-pepper noise
is low complexity - limitations : does not completely eliminate the edge points in 2D because it is sensitive to fine textures (1D pixel width), the pdf is not easy to calculate for any noise distribution (however numerical solutions can be found)