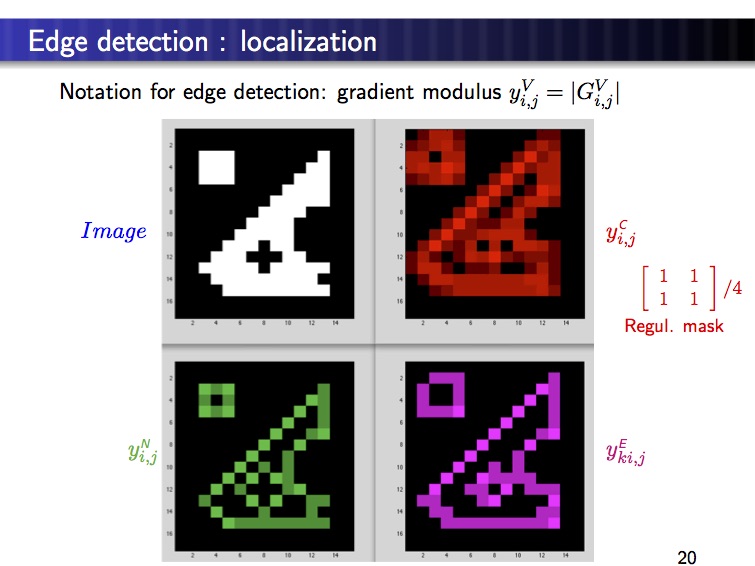
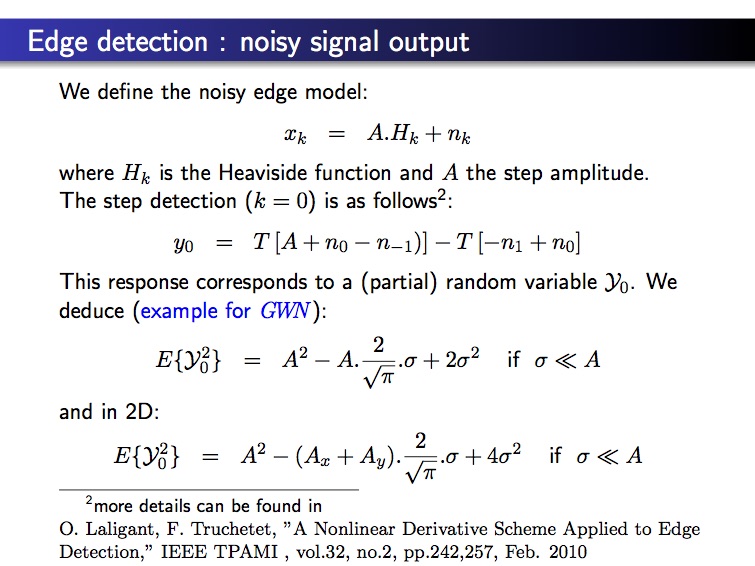
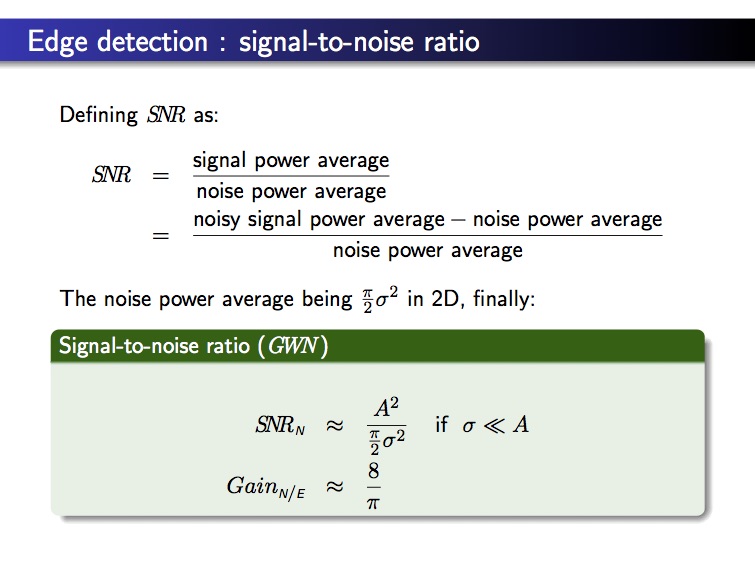
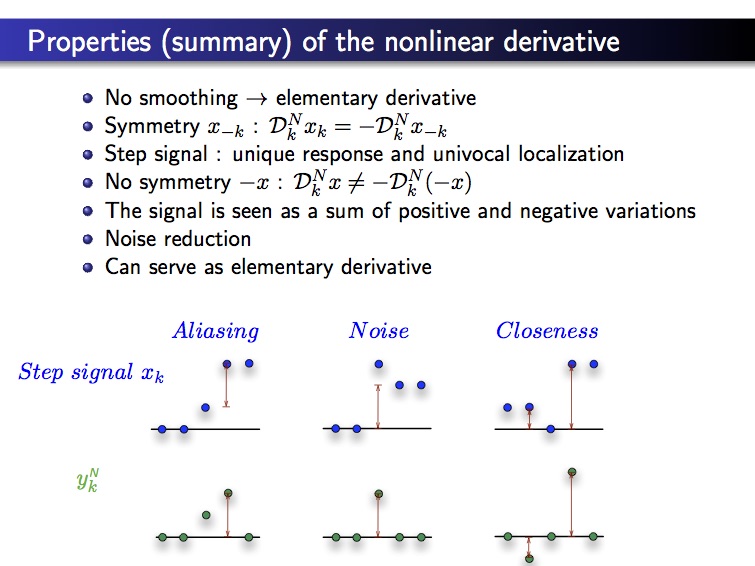
– edge detection –
– edge detection –
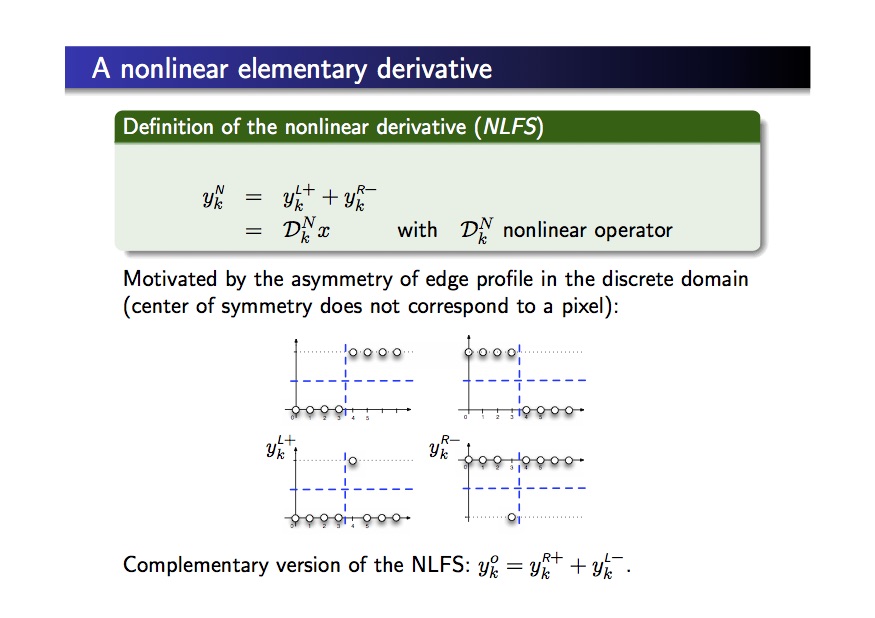
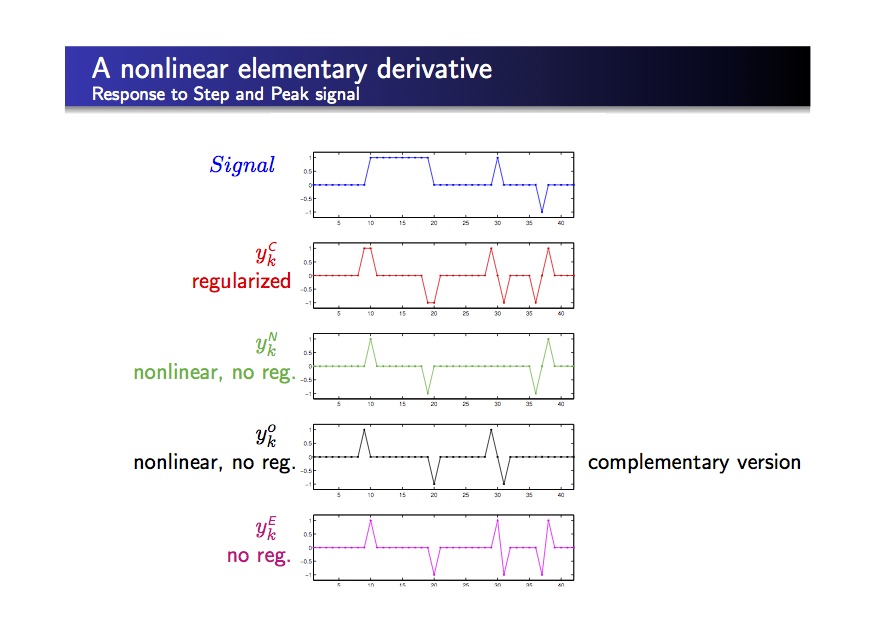
A NON LINEAR DERIVATIVE SCHEME APPLIED TO EDGE DETECTION (NLFS)
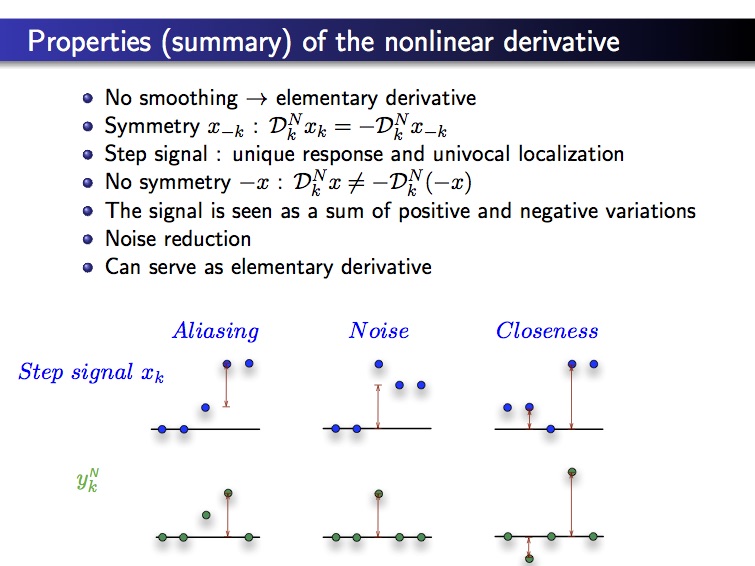
This new method presents the following properties:
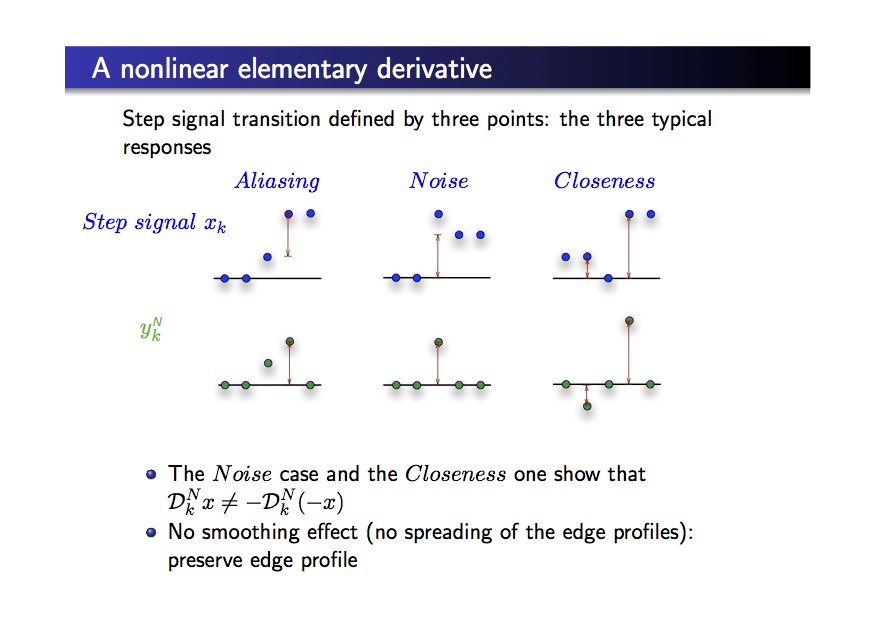
- univocal localization of edges
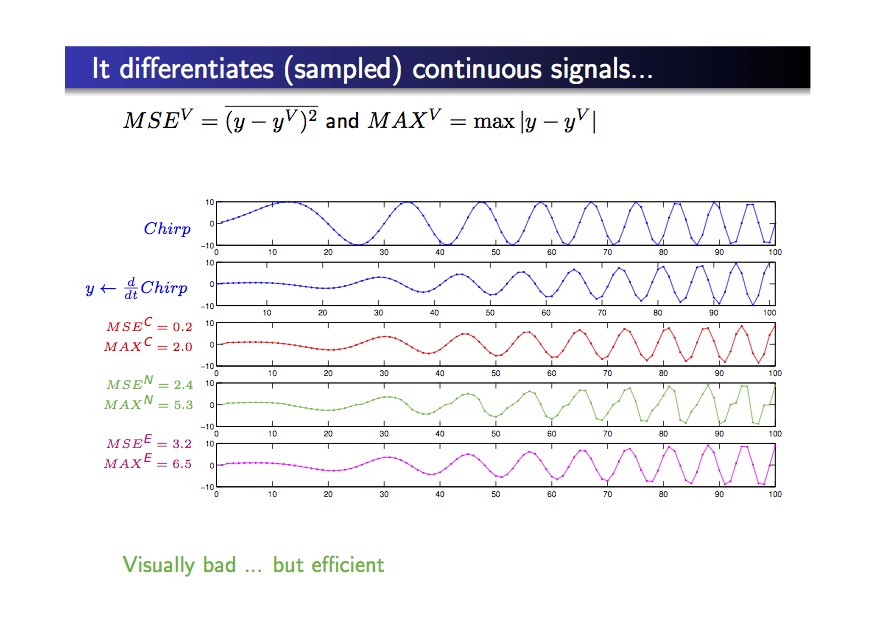
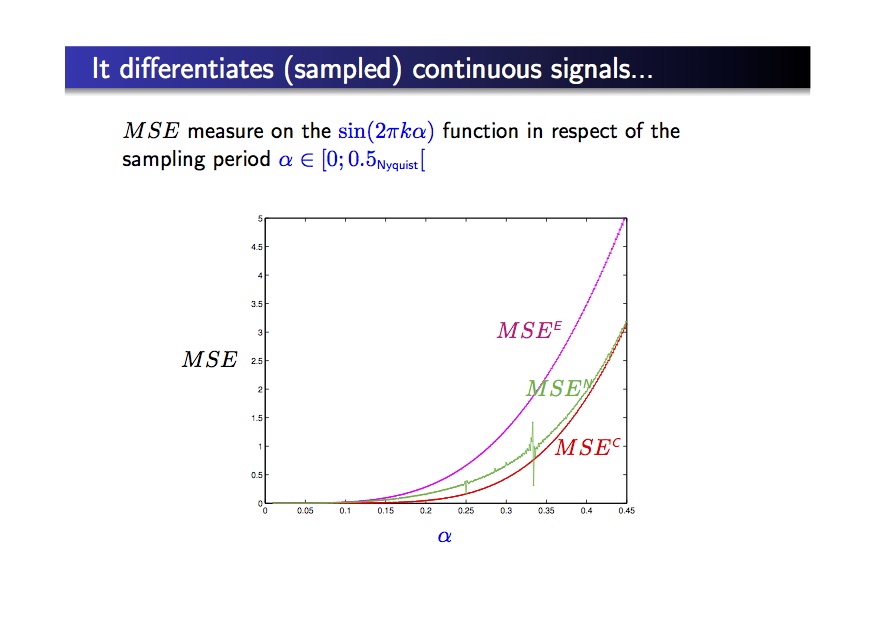
- all noise types reduction with no regularization: the noise level is weaker that the noise level in the original image
- better direction estimation of the gradien
- can product a confident edge reference map with synthetic images
- extremely efficient on salt noise OR pepper noise (this last case needs a change in the nonlinear derivatives) can integrate regularization in two ways
- still noise reduction with regularized schemes (Canny, Demigny, …)
- can also be adapted to the asymetrical filters (Prewitt, Sobel, …)
Ref: A Nonlinear Derivative Scheme Applied to Edge Detection, Olivier Laligant, Frederic Truchetet, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence – PAMI , vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 242-257, 2010. ![]()
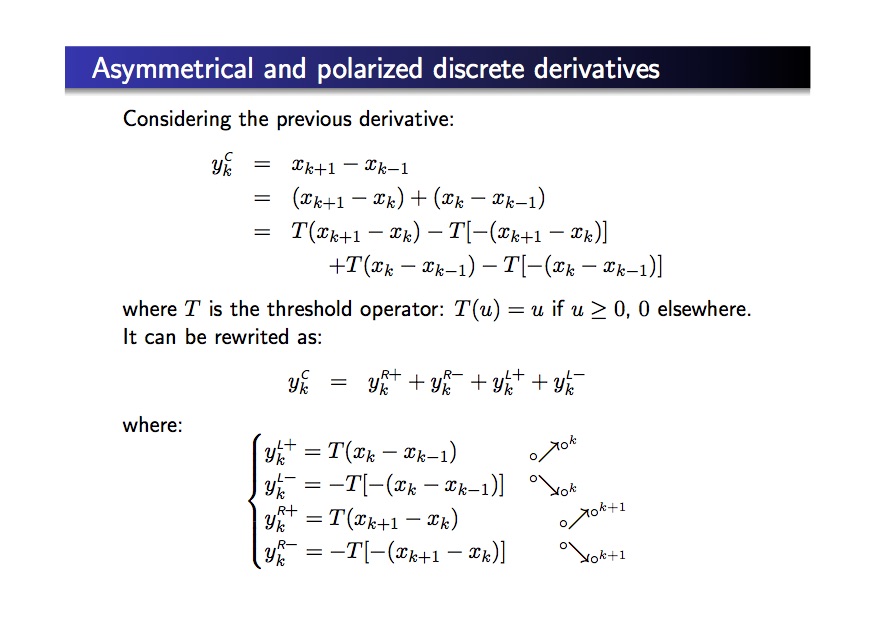
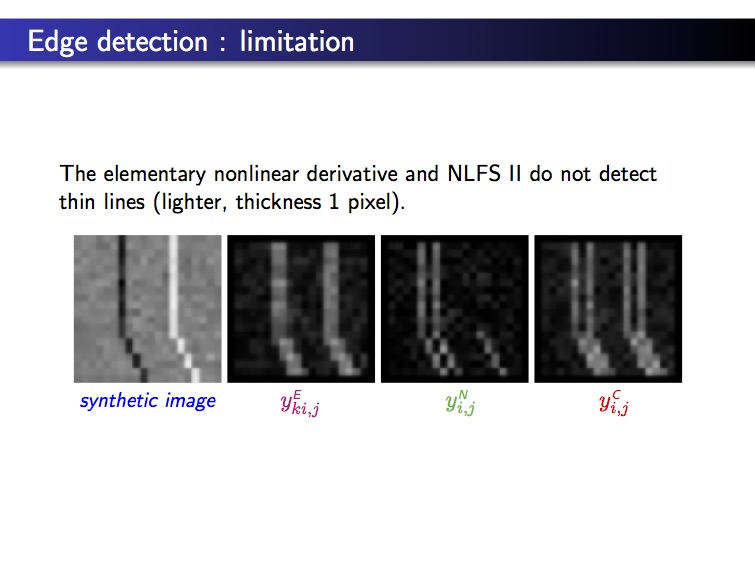
Why this new derivative ?
– Let us consider some classical approaches for edge detection:
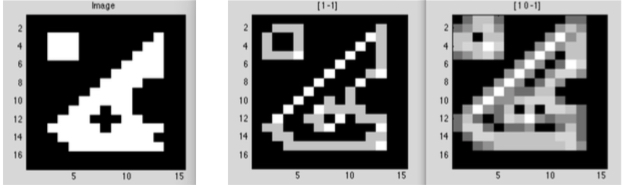
Gradient modulus on the « image » obtained by the derivatives [1 -1] and [1 0 -1]
 Binary edge images obtained with differentiating methods : Roberts (no regul. in Roberts), Prewitt, Sobel, Canny.
Binary edge images obtained with differentiating methods : Roberts (no regul. in Roberts), Prewitt, Sobel, Canny.
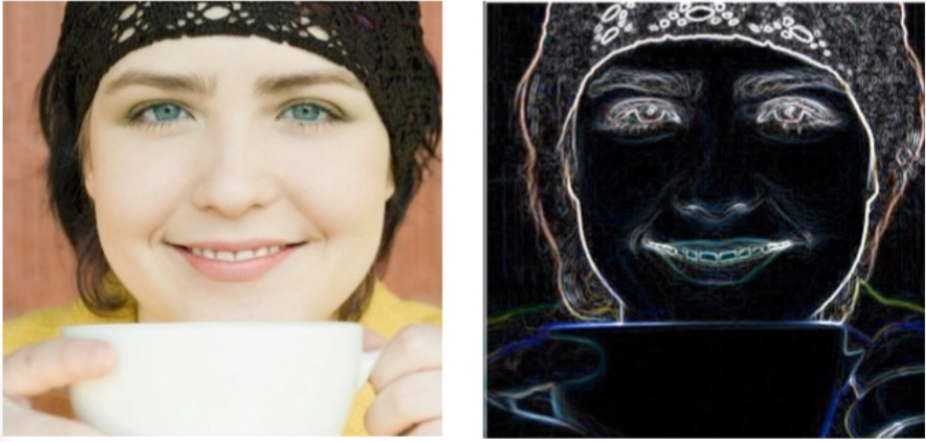
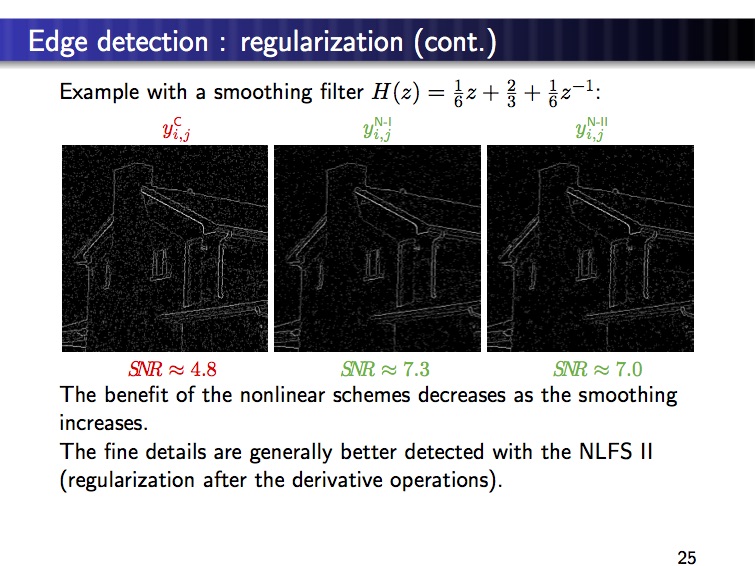
– The result with the proposed derivative (NLFS) is as follows: